How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone operation, from understanding regulations and pre-flight checks to mastering drone controls, capturing stunning aerial footage, and troubleshooting common issues. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies.
From understanding the legal framework governing drone flights in various countries to mastering the intricacies of drone controls and camera settings, this guide provides a structured approach to learning. We’ll explore different flight modes, techniques for capturing high-quality aerial imagery, and essential maintenance procedures to ensure your drone’s longevity. We’ll even touch upon advanced techniques and troubleshooting, preparing you for a wide range of scenarios.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local and international regulations. Failure to comply can lead to significant penalties, including fines and legal action. This section Artikels essential safety procedures and legal considerations for safe and compliant drone operation.
Drone Licensing and Certification Requirements, How to operate a drone
Drone licensing and certification requirements vary significantly depending on the country and the intended use of the drone. Many countries categorize drones based on weight and intended use, dictating the level of licensing needed. For recreational use, a simple registration might suffice, while commercial operations typically require more extensive certifications and licenses, often involving flight training and examinations.
Always check with your local aviation authority for the most up-to-date information specific to your region.
Drone Flight Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation demands a thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to strict safety protocols throughout the flight. This ensures both the safety of the drone and the safety of people and property in the surrounding environment. Negligence can lead to accidents and serious consequences.
- Pre-flight Checks: Inspect propellers for damage, ensure batteries are fully charged and properly connected, and confirm GPS signal acquisition. Check the weather conditions; avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
- During Flight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone at all times. Avoid flying near airports, crowds, or sensitive areas. Be mindful of airspace restrictions and adhere to altitude limits.
- Post-flight Procedures: Safely land the drone, power it down, and store it in a secure location. Review flight logs and imagery to identify any areas for improvement in future flights.
Legal Implications of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can result in various penalties, depending on the severity of the infraction and the jurisdiction. These penalties can range from warnings and fines to the confiscation of the drone and even criminal charges. Understanding and adhering to the regulations is crucial to avoid legal repercussions.
International Drone Regulations Comparison
Drone regulations vary considerably across countries. The table below offers a simplified comparison, but it is crucial to consult official sources for the most accurate and up-to-date information for your specific location.
| Country | License Required | Flight Restrictions | Penalties |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Registration required for most drones; Part 107 license for commercial operations | Restrictions near airports, stadiums, and other sensitive areas; altitude limits | Fines, drone confiscation, potential criminal charges |
| Canada | Registration required for most drones; Specific authorizations needed for commercial operations | Restrictions near airports, populated areas, and sensitive sites; altitude limits | Fines, drone confiscation, potential criminal charges |
| United Kingdom | Registration required for most drones; Permission for commercial operations | Restrictions near airports, populated areas, and sensitive sites; altitude limits | Fines, drone confiscation, potential criminal charges |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Preparations
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring a safe and successful drone flight. This checklist covers critical aspects of drone preparation, flight location selection, and sensor calibration.
Step-by-Step Drone Flight Preparation
Preparing your drone for flight involves a series of crucial steps designed to minimize the risk of malfunctions or accidents.
- Inspect the drone’s body and propellers for any damage. Replace any damaged components.
- Check the battery level and ensure it’s fully charged. Use only approved batteries for your drone model.
- Power on the drone and controller, ensuring a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Perform a pre-flight system check using the drone’s built-in diagnostics.
Selecting Appropriate Flight Locations
Choosing the right location for your drone flight is paramount for safety and legal compliance. Consider these factors before taking off.
- Weather Conditions: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow. Check the weather forecast before and during your flight.
- Airspace Restrictions: Be aware of airspace restrictions near airports and other sensitive areas. Use online resources like FAA’s B4UFLY (USA) or similar apps to check airspace availability.
- Obstacles: Identify and avoid potential obstacles such as trees, buildings, and power lines. Ensure a clear flight path.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and other sensors is critical for accurate flight performance and stability. Inaccurate calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior and potential crashes.
Pre-Flight Checklist Flowchart
A visual flowchart can aid in remembering all necessary pre-flight steps. Each step should be meticulously followed to minimize the chance of error.
- Inspect Drone for Damage
- Check Battery Level
- Acquire GPS Signal
- Calibrate Compass and IMU
- Perform System Check
- Check Weather Conditions
- Verify Airspace Restrictions
- Identify Obstacles
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls and navigation techniques is fundamental for safe and efficient operation. This section covers the basic controls, flight modes, and GPS navigation.
Drone Remote Controls and Functions
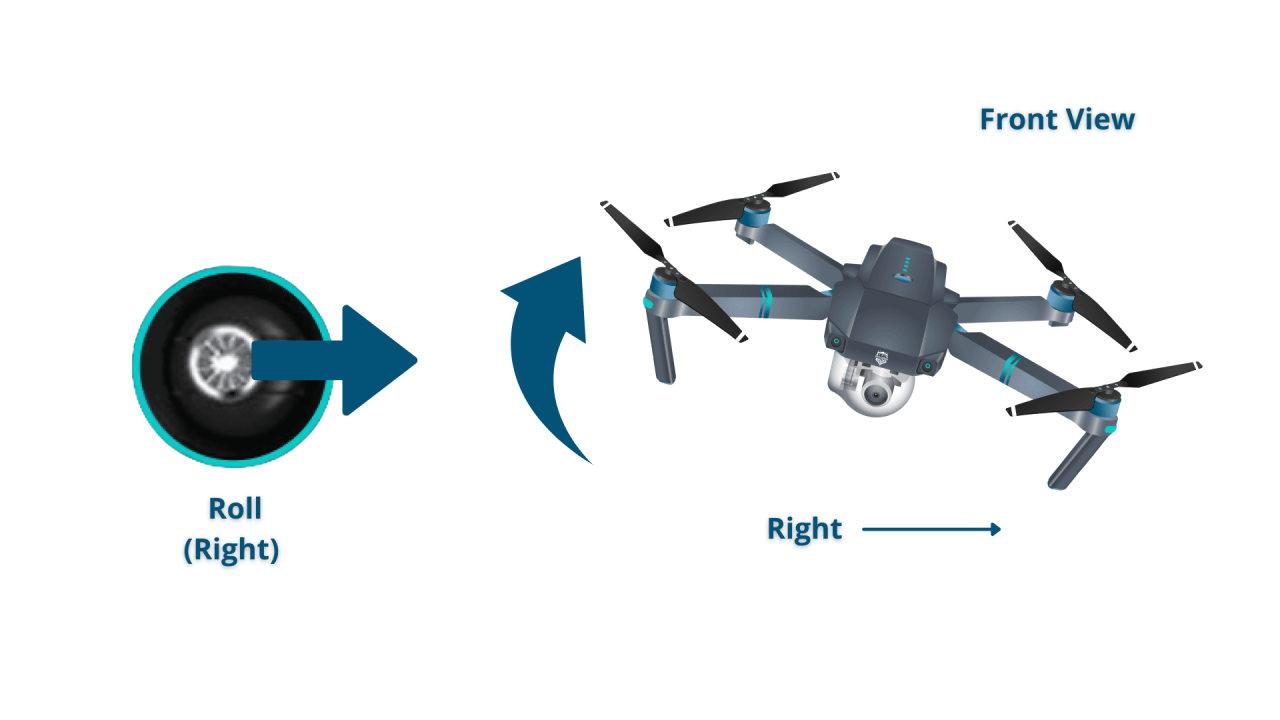
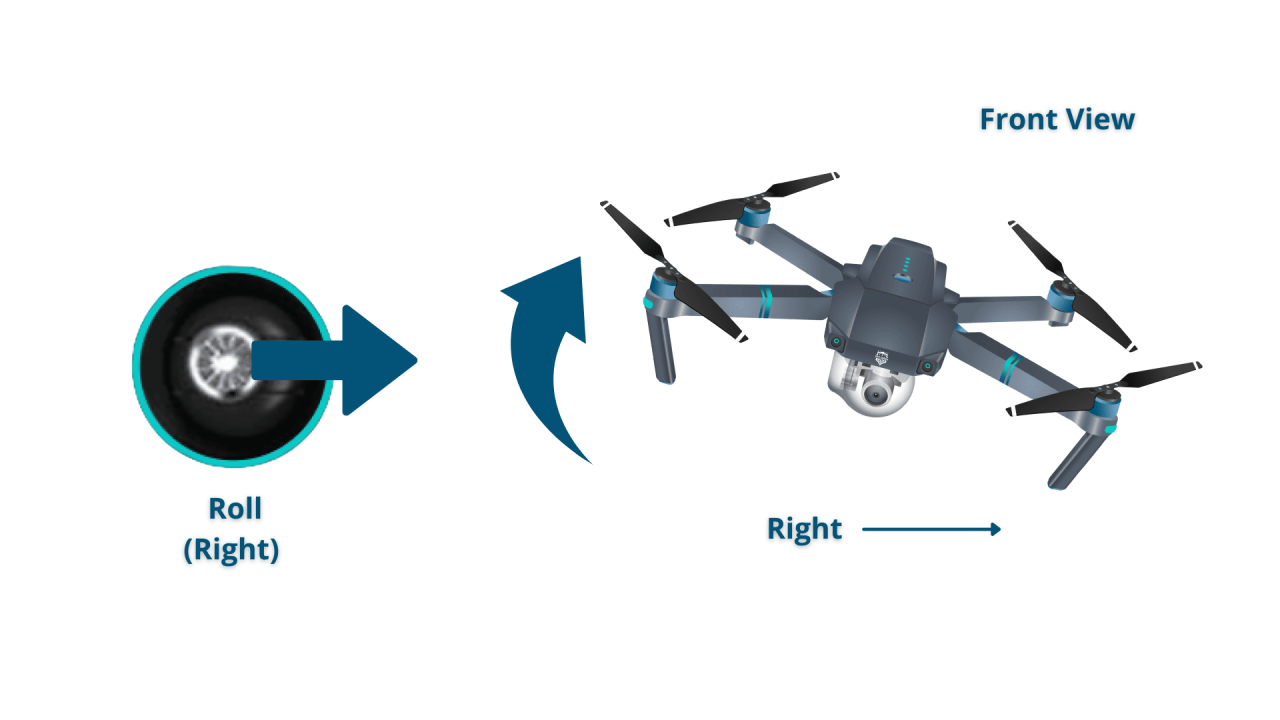
Standard drone remotes typically feature joysticks controlling throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. Understanding these controls is crucial for maneuvering the drone effectively and safely.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude.
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s movement forward and backward.
- Roll: Controls the drone’s movement left and right.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and autonomy. Choosing the appropriate mode depends on the pilot’s skill level and the complexity of the flight.
- GPS Mode: Maintains the drone’s position using GPS, ideal for stable hovering and precise movements.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s attitude (orientation) relative to its initial position, useful for more agile maneuvers.
- Manual Mode: Offers full control over the drone’s movement, requiring significant skill and experience.
GPS Navigation and Waypoints
GPS navigation allows for precise control over the drone’s flight path using coordinates or waypoints. This enables complex flight plans and automated maneuvers.
Drone Type Handling Characteristics
Different drone types, such as quadcopters and hexacopters, exhibit different handling characteristics. Quadcopters are commonly used for their maneuverability and ease of use, while hexacopters offer increased stability and redundancy.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding drone camera settings and employing effective photographic techniques.
Drone Camera Settings and Image Quality

Adjusting camera settings like shutter speed, aperture, and ISO significantly impacts image quality. Understanding their interplay is essential for achieving the desired results.
- Shutter Speed: Controls motion blur. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls depth of field. Wider apertures (smaller f-numbers) create shallow depth of field, while narrower apertures (larger f-numbers) create greater depth of field.
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values produce less noise but require more light, while higher ISO values are more sensitive to light but produce more noise.
Techniques for High-Quality Aerial Photography and Videography
Achieving professional-looking aerial footage requires careful consideration of composition, lighting, and other factors.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques to create visually appealing images.
- Lighting: Shoot during the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for soft, warm lighting.
- Framing: Pay attention to the background and ensure it complements your subject.
Common Issues and Solutions in Drone Photography and Videography
Various issues can arise during drone photography and videography. Understanding these problems and their solutions is essential for successful image capture.
- Overexposed Images: Reduce ISO or shutter speed.
- Underexposed Images: Increase ISO or shutter speed.
- Blurry Images: Increase shutter speed or use a tripod.
Best Practices for Storing and Managing Drone Footage
Properly storing and managing drone footage ensures its longevity and accessibility. Regular backups and organized file structures are vital.
- Regular Backups: Back up your footage to multiple locations (cloud storage, external hard drives).
- Organized File Structure: Create a clear and consistent file structure to easily locate your footage.
- Metadata: Add metadata to your files (date, location, description).
Troubleshooting and Maintenance: How To Operate A Drone

Regular maintenance and effective troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its reliable performance. This section addresses common malfunctions and maintenance procedures.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Several common malfunctions can occur with drones. Understanding their causes is the first step towards effective troubleshooting.
- Low Battery: Insufficient charging or battery degradation.
- GPS Signal Loss: Obstructions or interference.
- Motor Failure: Mechanical damage or overheating.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Troubleshooting drone problems requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause and implement appropriate solutions.
- Check Battery Level: If low, charge the battery.
- Check GPS Signal: Move to a location with a clear view of the sky.
- Inspect Motors: Check for any damage or debris.
Recommended Drone Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your drone and prevents potential malfunctions. A schedule should be followed based on frequency of use.
- Inspect Propellers: Check for cracks or damage before each flight.
- Clean Drone Body: Remove dirt and debris after each flight.
- Check Gimbal: Ensure smooth operation and proper calibration.
Common Drone Parts and Maintenance Requirements
| Part | Maintenance Frequency | Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Before each flight | Inspect for cracks or damage; replace if necessary. |
| Battery | After each flight | Charge fully; store in a cool, dry place. |
| Gimbal | Monthly | Check for smooth operation; calibrate if necessary. |
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced drone operation, encompassing complex flight planning, specialized applications, and safe landing techniques in challenging environments.
Planning and Executing Complex Drone Flights
Advanced drone operation involves planning and executing complex flights using waypoints and autonomous maneuvers. This requires careful planning and consideration of various factors.
- Waypoint Planning: Utilize flight planning software to create precise flight paths.
- Autonomous Maneuvers: Utilize the drone’s autonomous capabilities for complex maneuvers.
- Flight Simulation: Practice complex maneuvers in a simulator before attempting them in real-world scenarios.
Drone Applications
Drones find applications in diverse fields, from aerial photography to infrastructure inspection. Understanding these applications helps tailor drone operations to specific needs.
- Aerial Photography and Cinematography: Capturing high-quality aerial images and videos for various purposes.
- Infrastructure Inspection: Inspecting bridges, power lines, and other structures for damage.
- Search and Rescue: Assisting in search and rescue operations by providing aerial surveillance.
Creating and Executing Drone Flight Plans
Flight planning software simplifies the creation and execution of complex drone flights. These tools offer features for route planning, waypoint setting, and autonomous flight execution.
Safe Landing in Challenging Environments
Landing a drone safely in challenging environments, such as windy conditions or limited space, requires skill and careful planning. Practice and experience are essential.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has equipped you with the foundational understanding necessary to operate a drone safely and effectively. Remember to always prioritize safety, adhere to local regulations, and continuously refine your skills through practice and further learning. The sky’s the limit – but only with responsible operation.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires practice and a good understanding of safety regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including legal considerations and practical tips, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and effective drone piloting hinges on consistent practice and thorough knowledge of the machine.
Popular Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly quadcopters with GPS and beginner modes are ideal for beginners. Look for drones with features like automatic return-to-home.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires careful planning and practice, and a great resource to learn more is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide will help you build a strong foundation in safe and responsible drone operation, ensuring you can confidently take to the skies.
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, initiate a safe return-to-home procedure or carefully land the drone manually.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your local aviation authority’s website or contact them directly for information on specific drone regulations in your area.